Choosing a Non-Magnetic Fastener
 Non-magnetic fasteners play a crucial role in various applications where magnetic interference could disrupt processes or equipment. Common areas that require these fasteners include cryogenics, medical imaging like MRI machines, and certain military or scientific tools. This newsletter focuses on some specialized metal fasteners designed specifically for non-magnetic environments.
Non-magnetic fasteners play a crucial role in various applications where magnetic interference could disrupt processes or equipment. Common areas that require these fasteners include cryogenics, medical imaging like MRI machines, and certain military or scientific tools. This newsletter focuses on some specialized metal fasteners designed specifically for non-magnetic environments.
 Inconel Bolts
Inconel Bolts
Fasteners Known for Corrosion Resistance, High Strength, and Heat Tolerance
Inconel 625 and 718 bolts stand out in non-magnetic applications due to their unique properties. The Inconel 625 screws exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, rivaling even some grades of Hastelloy. With a tensile strength of 144 ksi and the ability to function at temperatures up to 1800°F, they are ideal for demanding environments. Meanwhile, Inconel 718 bolts boast twice the strength of Inconel 625, along with impressive creep-rupture capabilities up to 1300°F and operational limits reaching 1800°F.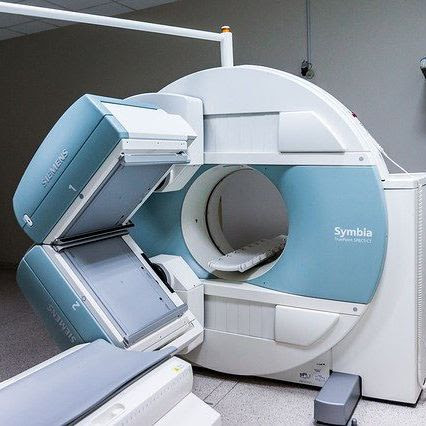 Titanium Bolts
Titanium Bolts
Lightweight, Strong, and Saltwater-Resistant Fasteners
Titanium grade 2 bolts offer superior resistance to chlorides and saltwater, making them suitable for use in both dynamic and stagnant seawater conditions. A titanium grade 5 bolt, on the other hand, is celebrated for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio—four times stronger than 316 stainless steel while being nearly half the weight. This makes it an excellent choice not only for marine applications but also in industries like medicine and defense. Aluminum 7075
Aluminum 7075
An Economical Option for Lightweight and Strong Non-Magnetic Fasteners
Widely used in aerospace applications, Aluminum 7075 bolts are prized for their combination of high strength and low weight. These screws provide strength comparable to many steel grades but at a fraction of the weight. Furthermore, Aluminum 7075 bolts can be heat-treated to meet different strength specifications, adding flexibility to their usage.
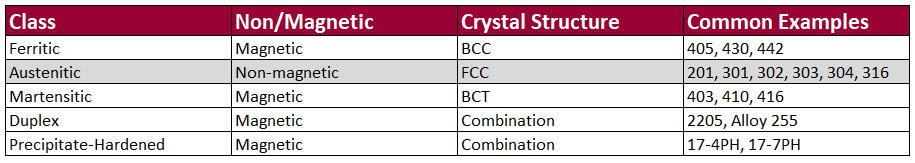
How Does Stainless Steel Fit into the Picture?

Common Non-Magnetic Applications
- Aircraft Maintenance & Overhaul
- Aluminum & Other Metal Smelting
- Applications Requiring Cryogenic Temperatures
- Electronics Manufacturers (Clean Room Maintenance)
- Hospitals & Clinics Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI- Maintenance on or near)
- Mine Sweepers
- Nuclear Products & Testing Machines
- Precision Magnetic Equipment (Compasses & Electronics – Maintenance on or near)
- Public Utilities: Gas, Electric & Telecommunication
- Radar Transmission Centers
Beyond the specific materials mentioned, there are countless other instances where non-magnetic fasteners are essential. For instance, any environment requiring precision without magnetic interference benefits from these specialized components. From ensuring the safety of nuclear reactors to maintaining sensitive electronics, the role of non-magnetic fasteners cannot be overstated.
As industries continue to evolve, the demand for innovative solutions in non-magnetic fasteners will grow. Engineers and manufacturers must stay ahead by understanding the unique properties of materials like Inconel, Titanium, and Aluminum 7075, ensuring they select the right fasteners for the job. Whether it's enhancing aircraft durability, improving MRI accuracy, or developing advanced radar systems, these fasteners remain indispensable.
solar panel is a device which converts solar radiation into electric energy directly or indirectly by absorbing sunlight through photoelectric effect or photochemical effect.
The main material of solar panels is silicon, most of the solar panels use silicon as the basic material, because silicon has excellent photoelectric conversion performance. However, due to the high production cost, silicon-based solar panels are not yet widely and universally used in large numbers. The working principle of solar panels is based on the photoelectric effect or photochemical effect, which converts light energy into electricity by absorbing sunlight. This conversion process allows solar panels to generate electricity wherever the sun shines, and is suitable for applications ranging from large power stations to small portable chargers. Solar panels are usually composed of a number of solar cells assembled on a board in a certain way to form an assembly, these components can be monocrystalline silicon or polycrystalline silicon, with different photoelectric conversion efficiency and characteristics. The output power of the solar panel directly depends on light intensity and light Angle, the greater the light intensity, the greater the working current of the solar panel, the higher the power generation efficiency. In addition, the installation and use of solar panels also need to consider the light Angle and occlusion factors to ensure the best power generation efficiency. With the advancement of technology and the development of materials science, the efficiency and longevity of solar panels continue to improve, making them play an increasingly important role in the global energy supply.
Solar Panel, Mini Solar Panel, 100W Solar Panel, 200W Solar Panel
Guangdong Dp Co., Ltd. , https://www.dp-light.com