Private enterprise owners collective anxiety, most of them ready to immigrate at any time
Zhu Tao has been in Shanghai for more than 20 years, starting from scratch, and today he is the largest channel in a chemical industry in China. His business is spread all over the world, and the largest domestic and foreign industry companies are his customers.
Zhu Tao’s anxiety is not an isolated case.
Shanghai New Shanghai Merchants Association, one of Shanghai's most influential private chambers of commerce, consisting of a group of Shanghai-based business celebrities and provincial-level chambers of commerce, and the Joint Zero Research Consulting Group's “2014 China Private Enterprise†for 150 private enterprises across the country. In the “Development Index†survey, it was found that in 2013, the index of security of Chinese private entrepreneurs only scored 6.09 points in the 10-point system and barely “passedâ€. The results of this survey show that “the uncertainty caused by policy fluctuations†is the main source of entrepreneurial insecurity, accounting for 31.5%.
However, since last year, the central government has carried out a series of reforms of decentralization and decentralization, which has increased the confidence of many private entrepreneurs in the future.
Talent anxiety
In 1989, Zhu Tao came to Shanghai with a train, smashed sandbags under the Nanpu Bridge, and later began to do chemical business with his fellow villagers. In the process of starting a business, he was almost killed by the triangular creditors, and he was also dragged into the prison by his peers. .
Therefore, today's career is regarded by Zhu Tao as life is generally important.
Companies need to continue to grow bigger and stronger and innovate. This year, Zhu Tao will lead the company into the era of e-commerce, which will be a revolutionary step for the traditional industry of chemicals. However, at the time of “Second Entrepreneurshipâ€, Zhu Tao discovered that with the advent of economic model changes, social changes were also unsuccessful, and the dividends such as population and funds that had benefited private enterprises had begun to recede.
The issue of human resources is becoming one of the most anxious issues for most private entrepreneurs. In 2013, private companies were deeply impressed by the operational pressures caused by rising labor costs. According to Deutsche Bank estimates, the average wage increase of grassroots employees in China in 2013 was close to 10%. 54.7% of the surveyed entrepreneurs surveyed believe that the increase in labor costs is not good for the company, and 14% is very unfavorable. The two add up to nearly 70%. In addition to wages, the additional costs are also raising labor costs. Take Zhu Tao’s enterprises as an example. The fees they paid on the “five insurance and one gold†project have been raised to 40% of the salary paid.
The lack of labor supply due to changes in demographic structure and the general increase in household income have led to the end of the “demographic dividendâ€. In 2012, China’s 15-59-year-old working population experienced the first decline since the 1970s, and it was reduced by 3.5 million. It is estimated that after 2023, the annual average will be reduced by about 8 million labor. In addition, the aging of the population has also accelerated.
Another key factor that has led to demographic changes is urbanization. Although China's greatest potential for future development is urbanization, nearly half of the above-mentioned entrepreneurs surveyed are worried about the “labor shortage†caused by urbanization.
Private enterprises are still generally untouched by talents. The two small things that happened last year made Zhu Tao feel very depressed. After he graduated, he entered his company. After half a year, he resigned and went to a foreign company. Just two days before he resigned, the company just gave him a good job in Shanghai. Hukou; another new employee, who has not signed the labor contract for a long time, one month later, the employee went to the labor department and took a bite, saying that the company did not sign the labor contract to illegally hire labor and demand compensation. "In many people's view, private enterprises are still a 'soft persimmon' that can be used." Zhu Tao said.
Wang Hongxin, executive director of the School of Overseas Education of Shanghai Jiaotong University, said that private entrepreneurs should be one of the most respected groups. Unfortunately, for various reasons, the society has always had misunderstandings about entrepreneurs, especially private entrepreneurs. Typical factors such as the original sin problem, the policy is not expected, the non-rigidity of private wealth protection, and the relationship between government and business have hindered the international expansion and the 100-year layout of a considerable number of entrepreneurs.
There are also banks that do not "wait to see" private enterprises. The difficulty of financing private enterprises is a common problem, but so far no cure has been seen. According to the “2012 China Entrepreneur Survival Index†conducted by Zero Research Consulting Group and Yabuli China Entrepreneur Forum, 85.1% of private entrepreneurs believe that the current financing policy is unfair, which is reflected in the application of state-owned enterprises and private enterprises. The status of bank loans is unequal.
In 2013, the state tried to crack the financing problem in guiding investment into circulation and supporting the real economy, such as trying to set up private banks by private capital. For the effectiveness of the policy, private enterprises will also wait and see.
complain
The macro environment, industry environment and internal management are the three layers of living space for enterprise development. According to a survey conducted by the Shanghai New Shanghai Merchants Association, in 2013, private companies interviewed generally “have confidence in themselves, have expectations for the industry, and are dissatisfied with the macro.†31.5% of entrepreneurs believe that “the uncertainty caused by policy fluctuations is the primary cause of their lack of securityâ€, which ranks first in the five categories. In addition, 10.7% and 10.1% of the interviewed entrepreneurs mentioned that “the legal system is not perfect†and “the social environment is not suitable for the development of private enterprisesâ€, resulting in a lack of security.
The "hands" of the government's market regulation are divided into two categories in the eyes of private enterprises. One is "free hands", the supervision is too broad, but the effect is not good; the other is "seeing Seeing the hand, this hand is too active, private enterprises from the industry policy, more feel the control, restrictions and containment.
This is most evident in the education, transportation and other industries. In various industries, the education and cultural industry has the lowest recognition of industry regulatory policies, and the most dissatisfied emotion among the industry is the administrative approval process.
Manager Zhao of an educational technology company in Beijing said that as far as he knows, the private enterprises under the name of “educational institutions†in Beijing are relying on the “enterprise training†business to maintain operations. “We really want to do education, but it’s hard to be in the real education industry. The approval process in this industry is too complicated and the threshold is too high.â€
Manager Zhao said that taking the private kindergarten as an example, it is necessary to meet the four conditions. First, it must have the qualification of a legal person before the application. If it is applied in the name of an individual, it must have the official residence registration in Beijing. Secondly, the business registration capital must be 10 million. Third, there must be a notarized economic risk guarantee, the guarantee amount is not less than the sum of the student fees for one year; in addition, school buildings, education and teaching facilities, equipment and teachers must be provided in accordance with national standards.
Even if you have the above qualifications, you still have to face the cumbersome bidding process, and the application procedures are more than 16, including the application for running a school, the capital verification report, and the certificate of the property rights of the school. There are more than 5 bidding procedures, including the Education Bureau and the Civil Affairs Bureau. The Public Security Bureau, the Local Taxation Bureau, and the Finance Bureau have more than six regulations.
In addition to complaints about market supervision, the dissatisfaction of private enterprises to the macro is also derived from the following points: First, the industry policy is not balanced. For example, state-owned enterprises and private enterprises do not receive fair treatment in industrial policies, large enterprises and small enterprises, Old enterprises and new enterprises have not been treated fairly; second, industry policies are unreasonable. For example, policy revisions and adjustments lag behind market changes, and the threshold for enjoying support policies is too high. Third, industry policies are over-expanded.
For policy support under the economic crisis, only one-third of private entrepreneurs recognize their positive effects. The survey results completed by the Research Department of the Shanghai Municipal Committee of the People's Republic of China show that in some special industries, the proportion of approved macroeconomic policies is relatively low. For example, only 23.8% of private enterprises in the education and cultural industries believe that the impact of government policies on their own companies is positive, and the proportion in the transportation and logistics warehousing industry is as low as 11.1%.
Yuan Yue, chairman of the Zero Research Consulting Group, pointed out that the “dreams of the government's support policies have not been taken into realityâ€, and there are basically two possibilities. First, private enterprises believe that there is no support policy, or that the role of supporting policies has not met expectations. Second, private enterprises believe that the support policies are opaque and the distribution is unfair. From the perspective of information channels, it is difficult for private enterprises to obtain government support policy information quickly and accurately. From the perspective of application channels, the threshold for some support policies is still high, and private enterprises have practical difficulties in applying.
Go to a dilemma
Immigration is a major consequence of the lack of entrepreneurial security. At the end of 2012, China Globalization Research Center and Beijing Institute of Technology Law School jointly released the China International Immigration Report (2012). The report shows that 27% of the ultra-high-net-worth enterprises with personal assets exceeding 100 million yuan have Immigrants, 47% are considering immigration, and nearly 60% of high-net-worth individuals with personal assets of more than 10 million yuan have completed investment immigration or have relevant considerations.
The above survey results also show that 33.3% of the entrepreneurs surveyed have or intend to immigrate, of which nearly 10% have successfully migrated and are applying for immigration.
The most direct reason for immigration for more than 80% of applicants is child education. Another 43% of the rich people regard the protection of wealth security as the second factor in investment immigration consideration. Seeking a higher quality of life, having more children, and lower tax rates are also considerations for investment immigration.
Most entrepreneurs are ready to do both. Zhu Tao believes that China will continue to be the world's largest market and a place for opportunities in the future. Therefore, his company will continue to be based in China. But at the same time, Zhu Tao also admitted that the year before, he had sent his daughter to the United States to study.
Blind flanges are made of carbon steel,stainless steel and alloy steel,etc.They are used to seal or block off a pipe,like a cover or cap.Because of its good overall performance, Flange is widely used in such basic projects as chemical engineering, construction, water supply, drainage, petroleum, light and heavy industry, freezing, sanitary, plumbing, fire protection, electricity, aerospace and shipbuilding.
Type: DIN2527
Pressure: PN6 to PN64
Material: Carbon steel or other required material
Surface: Original Color, Galvanizing or Paiting as clients requirements.
Packing: Wooden Cases
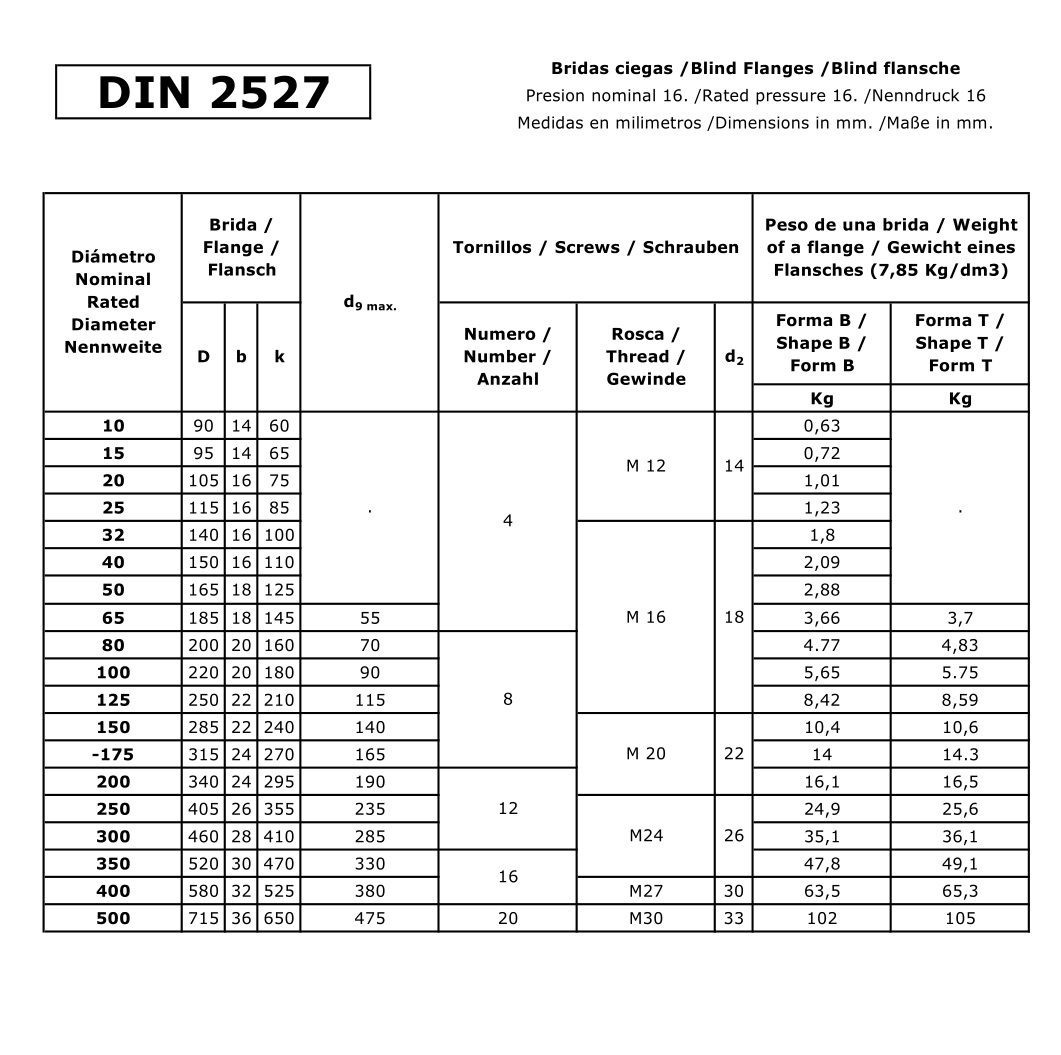
Drawing and data show DIN2527 PN16, if you need other pressures, please contact with supplier.
How to order: DIN number + (size) (x d1 dimension if not ISO) + (pressure) + material if not steel
Example: for steel = DIN 2527 DN 100 PN 16 Example: for stainless = DIN 2527 DN 100 PN 16 316SS
Blind Flange,Spectacle Blind Flange,Steel Blind Flange,Stainless Steel Blind Flange
HEBEI ZIFENG NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD. , https://www.zifengpipeline.com