Fastener thread knowledge practical articles sharing
What is a thread?
A thread is a shape having a uniform spiral protrusion on a section of the outer or inner surface of the solid.
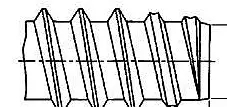
Section shape
The thread is divided into a triangular thread, a rectangular thread, a trapezoidal thread, and a zigzag thread according to its sectional shape (tooth shape).
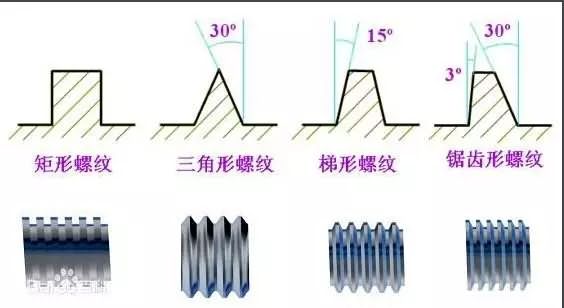
The triangular thread is mainly used for coupling (see threaded connection), and the rectangular, trapezoidal and zigzag threads are mainly used for transmission. Pipe threads are used for tight fitting of the pipe. Rectangular threads have high efficiency, but they are often difficult to grind, and the inner and outer threads are difficult to screw and center, so they are often replaced by trapezoidal threads. The working edge of the zigzag thread is close to the rectangular straight edge and is used to withstand the unidirectional axial force. The shape of the conical thread is triangular, mainly relying on the deformation of the tooth to ensure the tightness of the thread pair, and is mostly used for the pipe fitting.
Note:
The triangular thread has good self-locking performance. It is divided into coarse and fine teeth, and the general connection is mostly with coarse thread. (used to fasten wood) Fine teeth have small pitch, small lifting angle and better self-locking performance. They are often used in thin-walled tubes of small parts, with vibration or variable load connections, and fine-tuning devices.2, internal and external distribution
The external thread of the thread distributed on the outer surface of the mother body is called the internal thread on the surface of the mother body.
Eg: The thread on the surface of the bolt is the external thread, and the thread of the nut is the internal thread.
The internal thread of the same nominal diameter is larger than the external thread. Because the external thread is screwed into the internal thread.
Left internal thread, right external thread
3. Other classifications
The thread formed on the cylindrical body is called a cylindrical thread, and the thread formed on the cone body is called a tapered thread.
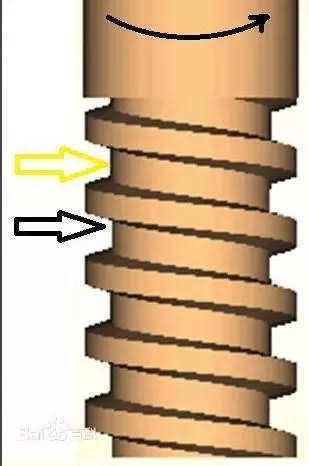
4, the direction of the spiral
The thread is divided into two types of left-handed and right-handed in the direction of the spiral, and generally uses a right-handed thread.
The left and right rotation is determined according to the needs of the mechanical device. The thread on the rotating part is considered to be anti-loose, and the direction of the thread is opposite to the direction of rotation of the part.Judgment method
1. Imagine placing the finger on the black arrow position in the image on the right. The thread turns yellow counterclockwise and turns yellow. When the arrow is used as a reference, the thread moves downward. So it is left-handed. 2. Place the thread vertically (both positive and negative), and the left side is the left-hand thread.
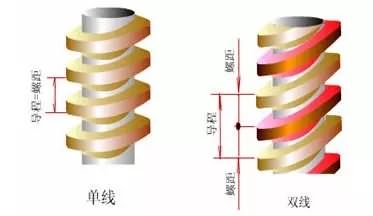
5, single and multiple lines
Threads can be divided into single-line and multi-wire.
Single thread:
A thread with only one spiral groove on the cylinder is called a single thread
Double thread:
The double thread is also called double thread, which means there are two spirals on the cylinder.
Most of the connections are single wires; when used for transmission, the speed is required to be fast or high, and double or multi-wire is used, but generally no more than 4 wires.
Single-thread thread has a small spiral angle (not easy to slide), and the friction between the screw and the nut is large (self-trimming ability), and the screw is used for locking, for example, fixing the screw of the ceiling fan, the gas bottle Fixed connection between parts in joints and mechanical equipment; etc.; multi-thread threads have a large angle of lift (easy sliding), and the friction between the screw and the nut is small, which is used to transmit power and motion, for example Lifting the wheel for maintenance of the wheel, bench vise for clamping the workpiece for bench work, and lathe screw for machining threads.
Important parameters
The main parameters of the thread are outer diameter (d), inner diameter (d1), medium diameter (d2), pitch (t), number of lines (n), lead (s=nt), angle of elevation (λ), and angle of the crown. (α) and so on. Except for the pipe thread with the inner diameter of the pipe as the nominal diameter, the other threads have the nominal diameter of the outer diameter.
Solder Connectors,Brass Soldered Connector,Forging Brass Connector,Brass Faucet Soldered Connector
JIANGMEN YILIN PRECISION MANUFACTURING CO.,LTD , https://www.ylseiko.com